New Networking Session
New Networking Session
The New-Networking Session is now ready for share at Computer-Networking Blog..
Visitors from all over the World are Warmly Wel-come to Visit and Share Networking Information With Every 1.....
Here Information Will Started From Basics and then move toward to Advance Level.
Visitors from all over the World are Warmly Wel-come to Visit and Share Networking Information With Every 1.....
Here Information Will Started From Basics and then move toward to Advance Level.
So be a part of Computer-Networking Blog and Enjoy the Whole Knowledge at your Own Pace.
Network Topologies
Network Topologies
A network topology is the physical layout of computers, cables, and other
components on a network.
There are a number of different network topologies, and a network may
be built using multiple topologies.
The different types of network layouts are Bus topology, Star
topology, Mesh topology, Ring topology, Hybrid topology and Wireless
topology.
Star Topology
Star Topology
A star topology is designed with each node (like workstations, printers
, laptops servers etc.,) connected directly to a central network hub/switch. Each
workstation has a cable that goes from the network card to
network hub or switch.
Advantages of Star Topology
• Easy to install and wire.
• No disruptions to the network then connecting or removing devices.
• Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
• Requires more cable length than a linear topology.
• If the hub fails, nodes attached are disabled.
• More expensive than linear bus topologies because of the cost of the
devices.
Common Network Cable types
Common Network Cable types
Cables are commonly used to carry communication signals within LAN. There are three common types of cable media that can be used to connect devices to a network and they are coaxial cable, twisted-pair cable, and fiber-optic cable.
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable looks similar to the cable used to carry TV signal. A solid-core copper wire runs down the middle of the cable. Around that solid-core copper wire is a layer of insulation, and covering that insulation is braided wire and metal foil, which shields against electromagnetic interference. A final layer of insulation covers the braided wire.
There are two types of coaxial cabling: thinnet and thicknet. Thinnet is a flexible coaxial cable about ¼ inch thick. Thinnet is used for short-distance. Thinnet connects directly to a workstation’s network adapter card using a British Naval Connector (BNC). The maximum length of thinnet is 185 meters. Thicknet coaxial is thicker cable than thinnet. Thicknet cable is about ½ inch thick and can support data transfer over longer distances than thinnet. Thicknet has a maximum cable length of 500 meters and usually is used as a backbone to connect several smaller thinnet-based networks.
The bandwidth for coaxial cable is 10 mbps (mega bits per second).
Twisted Pair Cable
Twisted-pair cable is the most common type of cabling you can see in todays LAN networks. A pair of wires forms a circuit that can transmit data. The pairs are twisted to provide protection against crosstalk, the noise generated by adjacent pairs. When a wire is carrying a current, the current creates a magnetic field around the wire. This field can interfere with signals on nearby wires. To eliminate this, pairs of wires carry signals in opposite directions, so that the two magnetic fields also occur in opposite directions and cancel each other out. This process is known as cancellation. Two Types of Twisted Pairs are Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) and Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP).
Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) cable is the most common networking media. Unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) consists of four pairs of thin, copper wires covered in color-coded plastic insulation that are twisted together. The wire pairs are then covered with a plastic outer jacket. The connector used on a UTP cable is called a Registered Jack 45 (RJ-45) connector. UTP cables are of small diameter and it doesn’t need grounding. Since there is no shielding for UTP cabling, it relies only on the cancellation to avoid noise.
UTP cabling has different categories. Each category of UTP cabling was designed for a specific type of communication or transfer rate. The most popular categories in use today is 5, 5e and 6, which can reach transfer rates of over 1000 Mbps (1 Gbps).
Optical Fiber Cable
Optical Fiber cables use optical fibers that carry digital data signals in the form of modulated pulses of light. An optical fiber consists of an extremely thin cylinder of glass, called the core, surrounded by a concentric layer of glass, known as the cladding. There are two fibers per cable—one to transmit and one to receive. The core also can be an optical-quality clear plastic, and the cladding can be made up of gel that reflects signals back into the fiber to reduce signal loss.
There are two types of fiber optic cable: Single Mode Fibre (SMF) and Multi Mode Fibre (MMF).
1. Single Mode Fibre (SMF) uses a single ray of light to carry transmission over long distances.
2. Multi Mode Fibre (MMF) uses multiple rays of light simultaneously with each ray of light running at a different reflection angle to carry the transmission over short distances
Network Infrastructure Devices
Network Infrastructure Devices
Hub
Hubs were the common network infrastructure devices used for LAN connectivity but switches are rapidly replacing hubs. Hubs function as the central connection point for LANs. Hubs are designed to work with Twisted pair cabling and normally use RJ45 jack to connect the devices. Network devices (Servers, Workstations, Printers, Scanners etc) are attached to the hub by individual network cables. Hubs usually come in different shapes and different numbers of ports.
When a hub receives a packet of data (an Ethernet frame) at one of its ports from a network device, it transmits (repeats) the packet to all of its ports to all of the other network devices. If two network devices on the same network try to send packets at the same time a collision is said to occur.
Bridges and Switchs
A bridge is a network device that operates at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) of OSI model. There are many different types of bridges and include Transparent bridges, Encapsulation bridges, Source-route bridges. Source-route bridges are for Token Ring network. Bridges allow segmenting a Local Network into multiple segments, thus reducing the network traffic. A bridge performs the segmenting function by examining the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) data packet (Ethernet Frame) and forwarding the packet to other physical segments only if necessary. Both swiches and bridges function using Data Link Layer (Layer 2) addressing system, also known as MAC addresses.
Bridge can connect only a few Networks, LANs or Hosts. A Bridge has comparatively less ports than a Switch. A Switch has usually 24 ports or 48 ports. Brides and Switches are considered to operate at Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of OSI model.
Router
A router is another network infrastructure device that directs packets through the network based on information from Network Layer (Layer 3) of OSI model. A router uses a combination of hardware and software to "route" data from its source to its destination. A router can be configured to route data packets from different network protocols, like TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, and AppleTalk.
Routers segment large networks into logical segments called subnets. The division of the network is based on the Layer 3 addressing system, like IP addresses. If the Network Layer (Layer 3) Data packet (IP Datagram) is addressed to another device on the local subnet, the packet does not cross the router and create a traffic congestion problem in another network. If data is addressed to a computer outside the subnet, the router forwards the data to the addressed network. Thus routing of network data helps conserve network bandwidth.
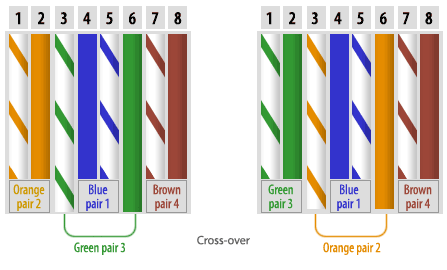
Straight-Through and Cross-Over cables
Straight-Through Cabling
CAT 5 UTP cabling usually uses only four wires when sending and receiving information on the network. The four wires, which are used, are wires 1, 2, 3, and 6. When you configure the wire for the same pin at either end of the cable, this is known as a straight-through cable.
Cross-Over Cabling
If we use want to connect two computers together with a straight-through cable, we can see that, the transmit pins will be connected to transmit pins and receive pins will be connected to receive pins. We will not be able to connect two computers or two hubs together using straight through cables.
Engineering:CommunicationSkills book
engineering book,engineering books,engineering E-books,electrical engineering,book, e book, e books, ebooks, enggineering ebooks, Engineering Books, engineering books download, free ebooks, free engineering books, jntu books, jntu e book, jntu ebooks, software engineering
MUST READ:- Knowing how to communicate clearly and effectively in the workplace is one of the keys to career success. "Communication Skills, Third Edition" focuses on the importance of solid speaking, writing, listening, and conversational skills for thriving in the workplace. Coverage also includes communication skills that are useful in specific situations, such as techniques for conducting structured and productive meetings. True-or-false quizzes in every chapter have been added to this edition as well as a new appendix of helpful Web sites. This helpful resource also features useful facts and statistics to help readers with their communication skills. The chapters include: Writing with a Purpose; Speaking with Confidence; Communicating Effectively; Good Communicators Are Good Listeners; and, Making Meetings Work.
Contents
Introduction
1 Writing with a Purpose
2 Speaking with Confidence
3 Communicating Effectively
4 Good Communicators Are Good Listeners
5 Making Meetings Work.
1 Writing with a Purpose
2 Speaking with Confidence
3 Communicating Effectively
4 Good Communicators Are Good Listeners
5 Making Meetings Work.
How to Remove shortcut Virus from Storage devices.
You may have faced an issue of virus infection while getting data from net cafes, from friend's laptops. Most of the time the you get the shortcuts of the folder or files present on storage system. The actual data is hidden in such case. Well known antivirus softwares are also failed to recover this virus. So here I have posted the ways to recover and get rid of such kind of problem forever. Take a look on it.
* Using Command Prompt
1. Click on Start menu, search for "Command Prompt".
2. Right click on it, and choose "Run as Administrator".
3. Suppose "E" is the letter for my connected usb device. Then you should write query on command prompt as:
2. Right click on it, and choose "Run as Administrator".
3. Suppose "E" is the letter for my connected usb device. Then you should write query on command prompt as:
attrib -h -r -s /s /d e:\*.*
or
attrib E:\*.* /d /s -h -r -s
or
attrib E:\*.* /d /s -h -r -s
Just copy paste above command in command prompt. Do not forget to change drive letter from above command.
* Using Free Applications
1. Download and install "UsbFix" from here.
http://www.fosshub.com/UsbFix.html
http://www.fosshub.com/UsbFix.html
2. If your antivirus not allowing this application to run, disable antivirus temporary from control panel.
3. Save any unsaved data.
4. Allow application to scan your devices. It will deplay infected files from your pc.
5. You can finally access log from "C:\UsbFix.txt".
3. Save any unsaved data.
4. Allow application to scan your devices. It will deplay infected files from your pc.
5. You can finally access log from "C:\UsbFix.txt".
* Using "AutoRunExterminator"
1. Download and install AutoRunExterminator from here.
http://en.kioskea.net/d…/download-11613-autorun-exterminator
http://en.kioskea.net/d…/download-11613-autorun-exterminator
2. Extract the files, double click on exe file.
3. The application will remain to run in background.
3. The application will remain to run in background.
* Using "Anti-malware"
1. Downoad and install Malwarebytes Antimalware from here.
http://en.kioskea.net/…/download-105-malwarebytes-anti-malw…
http://en.kioskea.net/…/download-105-malwarebytes-anti-malw…
2. Update the database.
3. Perform full scan.
3. Perform full scan.
200GB microSD card announced by SanDisk !!!
SanDisk Corporation has introduced the 200GB SanDisk Ultra® microSDXC™ UHS-I card, Premium Edition – the world's highest capacity microSD card for use in mobile devices. Just one year after its record-breaking 128GB microSD card, the company has increased storage capacity by 56% within the same fingernail-sized form factor. Blazingly fast transfer speeds of 90MB/s enable consumers to move up to 1,200 photos per minute.
The 200GB SanDisk Ultra microSDXC UHS-I card, Premium Edition, features a ten-year limited warranty and will be available worldwide in Q2 2015 at a suggested retail price of $399.99.
The 200GB SanDisk Ultra microSDXC UHS-I card, Premium Edition, features a ten-year limited warranty and will be available worldwide in Q2 2015 at a suggested retail price of $399.99.
This could be the world’s toughest flash drive
Green House has designed what could be the world’s toughest flash drive. The flash drive is said to be able to withstand and still work in temperatures of down to -40 degrees centigrade and up to as much as 85 degrees centigrade.
So in theory this means that wherever you were to take it on Earth, your data and files should be safe. However whether you would find a computer that would still work at -40 degrees centigrade that you could plug the flash drive into is another thing entirely.
Visually it doesn’t appear to have anything different about it from any other flash drive on the market. It hasn’t been covered in layers of insulation to make sure it works in very cold weather. Instead, Green House chose to put advanced error detection into the flash drive that can repair data automatically while the data is being copied. At the same time it can remember where any bad blocks are on the drive and not use them.
In order to prolong the lifespan of the drive, the drive also makes sure than data is written across all of the drive to avoid wear.
It is going to be released in a 16GB offering and it isn’t the fastest out there as it reads and writes at transfer rates of as much as 27MB per second and 23.9MB per second. So if you are planning a trip to the Arctic circle and you need a flash drive to transfer and store your photos on, this could be the one, providing your camera doesn’t freeze.
Virtual reality jetpack training for astronauts
Virtual reality has been hitting the spotlight a lot lately; Google announcing the halt in production of Glass, Microsoft unveiling the HoloLens and LG offering free virtual reality headsets with every purchase of a G3 smartphone. Well this one trumps them all as it’s out of this world, literally. This image shows how astronauts go through virtual reality jetpack training in the ISS in case they ever need to stop themselves drifting off into space.
And in much the fashion of Google Carboard and LG’s virtual reality offering, a laptop (not a smartphone) is housed in a virtual reality headset and strapped to the astronaut’s face. But don’t let that fool you on its performance of the virtual reality simulator, it’s said to be far more substantial than the headsets we’re using down here on Earth.
Jetpack training is pretty expensive and you probably wouldn’t want to run the risk of training out in space in case something went wrong (how else are you going to practice low gravity jetpack training?). They are training to use jetpacks known as Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue, or “SAFER”, that astronauts use to go to locations far from the ISS.
USE YOUR PENDRIVE AS YOUR SYSTEM RAM
USE YOUR PENDRIVE AS YOUR SYSTEM RAM
2) Wait for the Pen Drive Detection and see whether it is detected or not
3) After detection of Pen Drive, you should do the following things Carefully
4) Now go to My Computer and right click it, then go to the Properties
5) Now go to Advanced and then to the Performance settings
6) Now again Advanced, and go to Change
7) In the Change, select the pen drive which u inserted
Then click on the Custom size and " check the value of space available "
9) Please Enter the Same in the Initial and Maximum Columns also
10) Now your Pen drive space is used for the System Virtual Memory , Just Restart and enjoy the Faster and Furious PC
MUST SHARE & LIKE Interesting Engineering PAGE
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)